Delving into Gut health and its connection to brain function, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative. The intricate relationship between our gut health and brain function is a fascinating topic that sheds light on the profound connection between two vital aspects of our well-being.
Through this exploration, we uncover the secrets of how our gut influences our brain and vice versa, paving the way for a deeper understanding of our overall health.
As we delve deeper into this discussion, we unravel the mysteries behind how what we eat can impact how we think and feel, highlighting the intricate mechanisms at play within our bodies.
Introduction to Gut Health and Brain Function
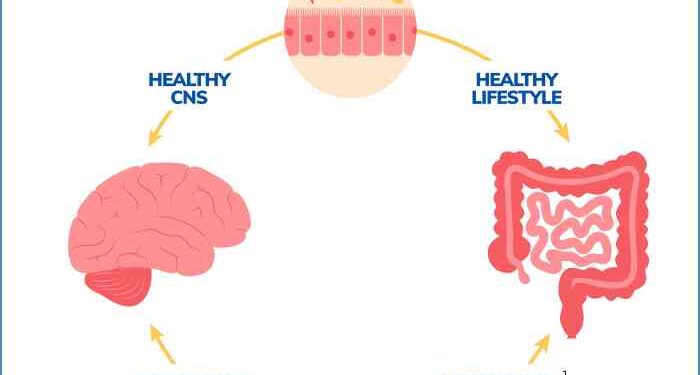
Understanding the intricate relationship between gut health and brain function is crucial for overall well-being. The gut, often referred to as the "second brain," plays a significant role in various bodily functions beyond digestion.
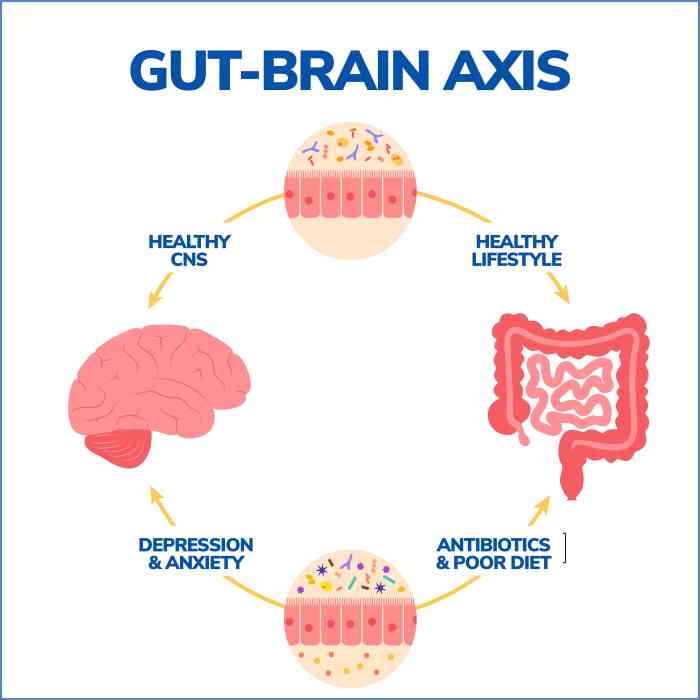
The Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a complex bidirectional communication system that links the gut and the brain. This connection involves neural, hormonal, and immunological signaling pathways, allowing for constant communication between the two organs.
- The Vagus Nerve: One of the primary communication pathways between the gut and the brain is the vagus nerve. This nerve transmits signals in both directions, influencing various physiological processes and emotional responses.
- Microbiota Influence: The gut microbiota, comprising trillions of bacteria, also play a crucial role in the gut-brain axis. These microbes produce neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, that impact mood and cognitive function.
- Immune System Interaction: The immune system in the gut can trigger inflammatory responses that affect the brain, leading to conditions like depression and anxiety. This highlights the close relationship between gut health and mental well-being.
The Impact of Gut Microbiota on Brain Function
The relationship between gut microbiota and brain health is a fascinating area of research that has gained significant attention in recent years. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being.Gut bacteria can influence mood, cognition, and behavior through various mechanisms.
For example, certain gut microbes produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which is known as the "feel-good" hormone. Imbalances in gut microbiota composition have been linked to mood disorders like anxiety and depression.Furthermore, gut bacteria can produce metabolites that can affect brain function.
Short-chain fatty acids, produced by gut bacteria during the fermentation of dietary fiber, have been shown to have neuroprotective effects and can help improve cognitive function.
Mechanisms of Gut Microbiota's Influence on Brain Function
- Production of neurotransmitters: Gut bacteria can produce neurotransmitters that affect mood and behavior.
- Regulation of inflammation: Imbalances in gut microbiota can lead to chronic inflammation, which has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
- Modulation of the immune system: Gut bacteria play a key role in regulating the immune response, which can impact brain health.
- Production of short-chain fatty acids: These metabolites have been shown to have neuroprotective effects and can improve cognitive function.
Factors Affecting Gut Health and Brain Function
Maintaining a healthy gut and optimal brain function is influenced by various lifestyle factors, with diet playing a crucial role in this intricate relationship.
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Gut Health and Brain Function
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of gut microbiota, leading to inflammation and affecting cognitive function.
- Sleep: Inadequate sleep can alter gut bacteria composition and impair brain function, including memory and decision-making.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise promotes diversity in gut microbiota, which is beneficial for both gut health and cognitive abilities.
Role of Diet in Gut Health and Brain Function
Diet plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy gut and supporting optimal brain function. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and antioxidants can positively impact gut microbiota and cognitive performance.
Foods that Promote Gut Health and Support Cognitive Function
- Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut are rich in probiotics that support gut health and may improve cognitive function.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are packed with antioxidants and fiber that benefit gut health and brain function.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and are essential for brain health.
Strategies to Improve Gut Health for Better Brain Function
Improving gut health is essential for optimizing brain function. By incorporating certain strategies into your lifestyle, you can support a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn benefits cognitive function and overall brain health.
Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Fermented Foods
Including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi in your diet can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. Prebiotic foods such as garlic, onions, bananas, and whole grains provide the necessary fiber to support the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Additionally, fermented foods like kombucha and miso can introduce beneficial probiotics to your gut, further enhancing its health.
The Importance of Hydration
Adequate hydration is crucial for both gut and brain health. Drinking enough water helps maintain the mucosal lining of the intestines, supports digestion, and aids in nutrient absorption. Dehydration can lead to constipation and hinder the elimination of toxins, negatively impacting gut health and cognitive function.
Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day to keep your gut and brain functioning optimally.
Creating a Gut-Friendly Diet
To enhance overall brain function, focus on consuming a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. Limit the intake of refined sugars and processed foods, as they can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria.
Including a variety of colorful foods in your diet ensures that you are getting a diverse range of nutrients that support both gut and brain health.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the intricate dance between gut health and brain function unravels a captivating story of interconnectedness and balance within our bodies. By nurturing our gut, we unlock the potential for a sharper mind and a healthier body, emphasizing the importance of paying attention to both aspects for overall well-being.
Expert Answers
What role does stress play in affecting gut health and brain function?
Stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to digestive issues and impacting brain function negatively. Implementing stress-reducing techniques can help improve both gut health and brain function.
Can gut health affect mental health conditions like anxiety and depression?
Yes, an imbalance in gut bacteria can contribute to mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. Taking care of gut health through a balanced diet and probiotics can potentially alleviate symptoms.
How does exercise influence gut health and brain function?
Regular exercise can positively impact gut health by promoting diversity in gut microbiota, which in turn can enhance brain function by reducing inflammation and improving mood.